FIO: Enabling Crypto Adoption through Usability
Key Insights
FIO is a protocol that enables a uniform user experience when transacting value across blockchains and products.
Its usage is enabled by crypto endpoints such as wallets, payment processors, and exchanges that integrate FIO capabilities.
FIO seeks to drive adoption via a user-friendly crypto experience.
On Usability
The rise of digital assets is following a similar trend as the Internet's growth in its day: as adoption increases, usability improvements follow behind. While it’s appealing to own a piece of a protocol via its tokens, sending tokens is often cumbersome and error-prone. Take, for instance, sending tokens to the wrong address or the constant juggling between user interfaces and wallets.
FIO protocol is a viable solution to improve usability without compromising on decentralizati
on — it offers a homogeneous user experience when transacting value across various blockchains and products. FIO uses human-readable wallet names to send, receive, and request digital assets.
FIO offers three core functionalities to improve usability: (1) handles, (2) requests, and (3) data.
First, FIO Crypto Handles are like email addresses for digital assets. Danielle@messari is a human-readable wallet name consisting of a username (Danielle) and a domain (@messari). Both usernames and domains are NFTs that substitute long public blockchain addresses. This reduces the risk of common mistakes such as sending tokens to the wrong address.
Second, FIO Requests are like https requests, but they are designed to preserve self-sovereignty. The request function allows users to request payments from other users, e-commerce order carts, or invoices. The prerequisite for this function is that both the sender and the receiver are utilizing FIO-enabled wallets. In terms of usability, FIO Requests are similar to using Paypal or Venmo.
Third, FIO Data is metadata that can accompany any blockchain transaction using a FIO-enabled application. For instance, FIO Data enables requesting or sending invoice payments with cross-chain metadata that specifies what the invoice is for. The metadata is useful, for instance, when including an order cart or when referencing off-chain data. Other uses of metadata include full auditability and adding transaction details for legal and compliance requirements.
Besides the three functionalities above, FIO offers an additional level of verifiability when protecting digital property. NFTs on any blockchain may be mapped to FIO Crypto Handles and FIO Domains. In this sense, FIO supports human-readable signatures as verification for digital property of NFTs created on any blockchain.
Technology in a Nutshell
FIO is a standalone decentralized usability layer that can be integrated by any crypto product. The FIO Protocol is open and permissionless: be it wallets, exchanges, or payment processors, none of them require any permission to integrate with FIO.
The Guts of FIO Crypto Handles and Domains
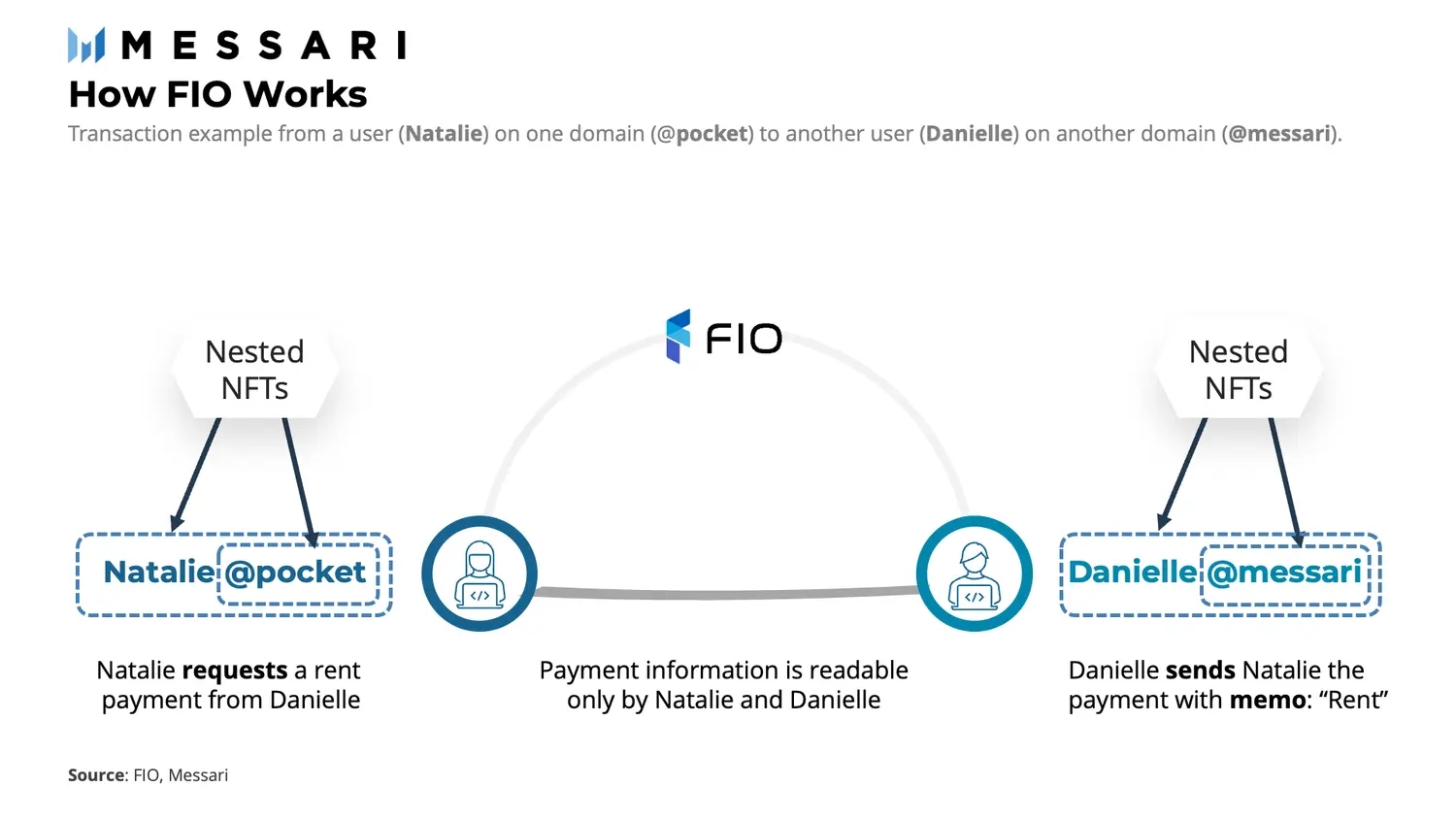
FIO Crypto Handles and Domains are nested NFTs: for instance, the natalie@pocket Crypto Handle has a different private key than the @pocket domain. Like an email domain, a FIO Domain may be public or private. For example, anyone can register a public gmail.com address because Google has made it open to do so. Similarly, a FIO Domain can be set to open status on the FIO blockchain by the private key holder, which would allow any FIO Protocol user to register a username on the @pocket FIO Domain (e.g., natalie@pocket). A closed FIO Domain would be similar to a domain like messari.io because only Messari can give permission for email addresses to be created with that domain. Private FIO Domain owners must sign a transaction on the FIO blockchain to approve the registration of a FIO Crypto Handle thereon.
All of a user’s wallet addresses can be mapped to a single Crypto Handle. Whether Natalie is transacting on Ethereum, Solana, Avalanche, etc., the FIO Crypto Handle natalie@pocket will do the job. Mapping involves signing a transaction on the FIO blockchain that links a public wallet key to a natalie@pocket Crypto Handle. This process is entirely non-custodial, as the FIO Protocol does not know the associated private keys. The mapping process is similar for addresses, NFTs, and even, in the future, fiat bank accounts.
Transactions and Requests
Once a public key has been mapped to a Crypto Handle, any FIO-enabled transaction feels like sending an email. Users can ignore the underlying mechanisms and complex public addresses, because, from their point of view, they are just sending tokens from one party to another. Through this level of usability, the FIO Protocol enables users to transact on-chain within their favorite crypto product as easily as making a Venmo or PayPal transaction.
FIO request functionality has an additional layer of logic that uses Diffie–Hellman encryption to create a shared secret between a requester and requestee. The requester signs a transaction with encrypted metadata specifying the token amount, the Crypto Handle that will send the funds, and any associated data (e.g., a note, invoice, or order cart). The requestee’s FIO-enabled product queries the FIO blockchain searching for requests. Following an in-app notification, the request is decrypted using their FIO private key. At this point, the user may choose to decline or accept the request. Should they accept an incoming transfer request, the transaction is made directly on the blockchain of choice from within the wallet. This transaction is entirely independent — as the FIO Protocol does not have access to user private keys.
Network Usage and Economic Value
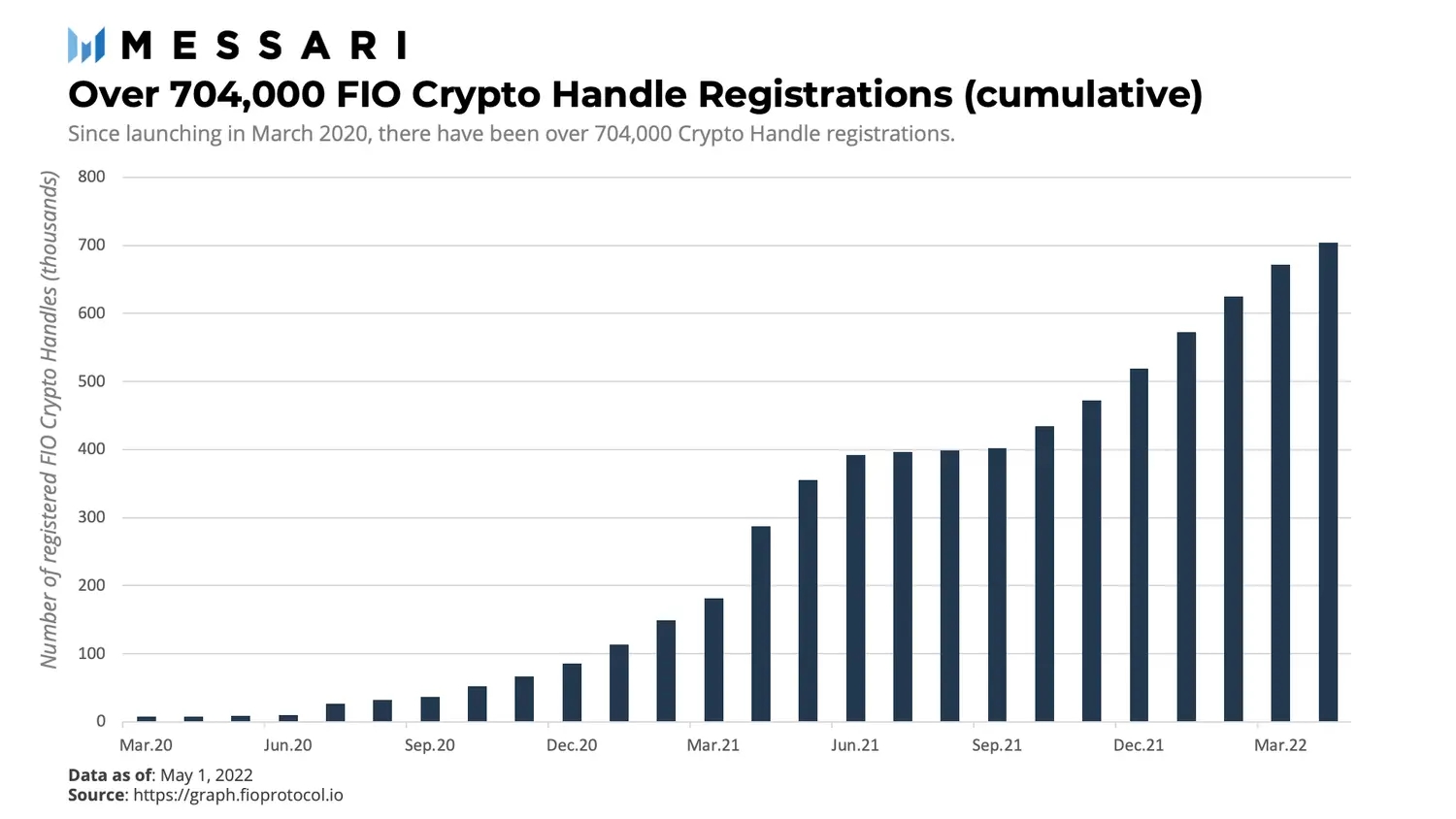
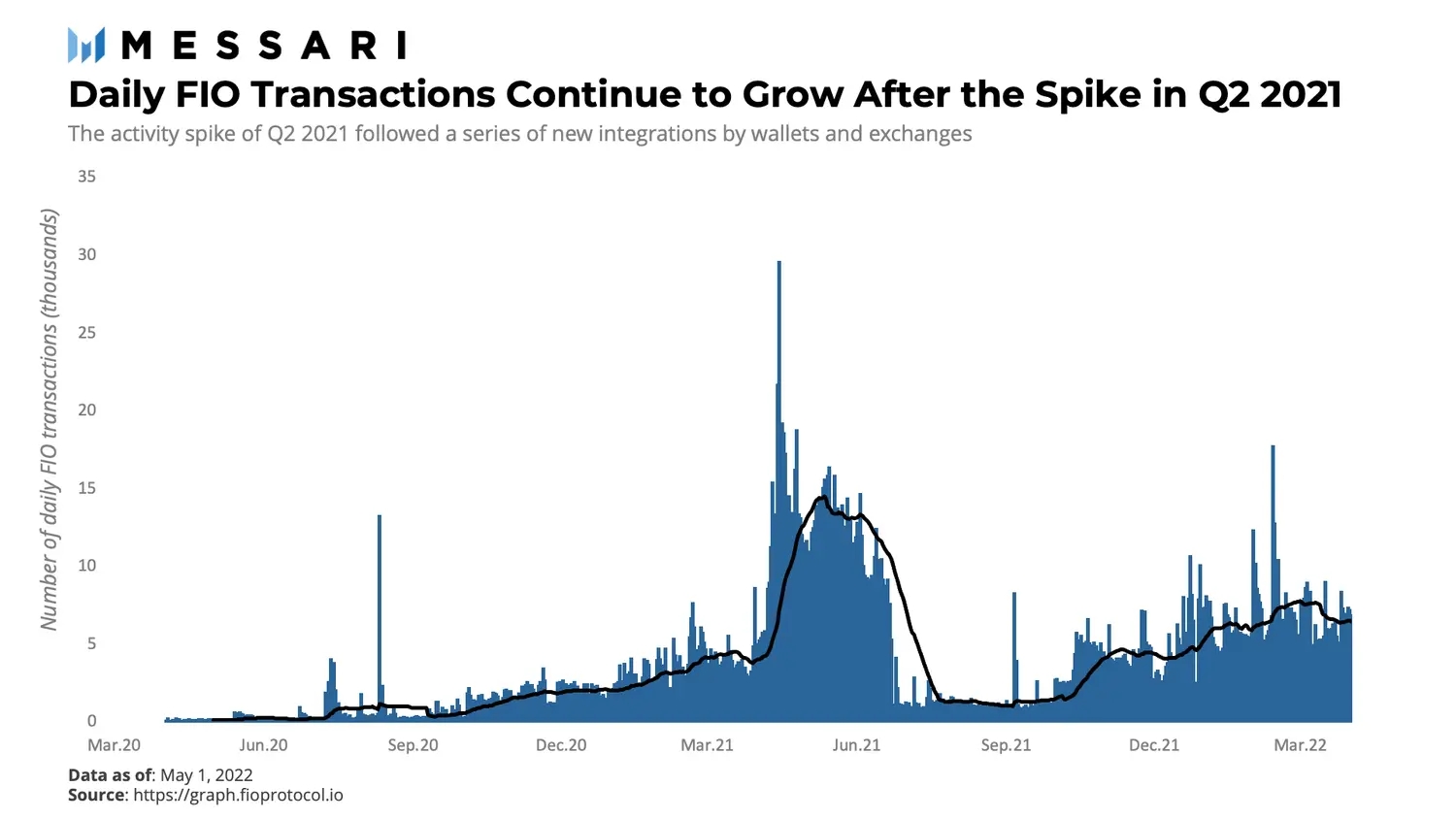
FIO has seen a steady inflow of new Crypto Handle registrations ever since its launch in March 2020. More than two years later, on May 1, 2022, there were a total of over 704,000 FIO Crypto Handle registrations, out of which over 459,000 are presently active.
There has generally been an upward trend in the number of daily transactions leveraging the FIO Protocol, and several activity spikes following new integrations by wallets and exchanges.
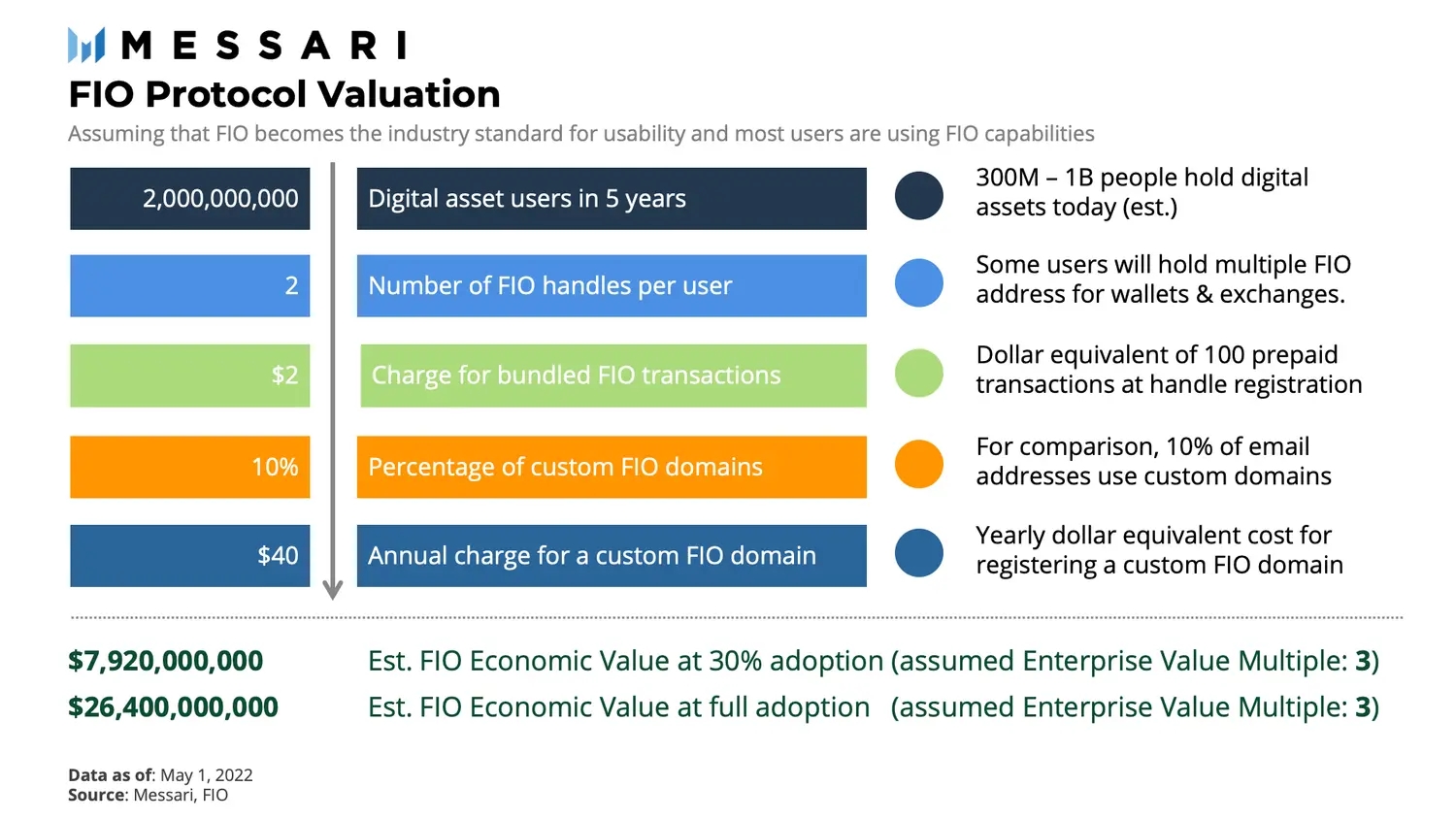
Next, let’s assess FIO’s potential market opportunity. In an ideal scenario, the FIO Protocol will be used as the standard usability layer for transacting digital assets. Unlike many Web2 applications that generate revenue solely from transaction fees, FIO uses annual charges on custom FIO Domains as well as prepaid bundles of transactions when registering FIO Crypto Handles. Below we depict a scenario for deriving the FIO economic value based on adoption assumptions.
According to Metcalfe’s law, the FIO network value can be considered to be proportional to the square of the number of active FIO Crypto Handles. The underlying assumption is that the number of transactions and their volumes will grow on par with the square of the number of active FIO Crypto Handles. Outside of Metcalfe’s law, future enhancements to the FIO Protocol may open the door to more utility fees in return for additional user value.
FIO Token and Its Tokenomics
The FIO community launched the FIO Protocol blockchain and token in April 2020. The FIO token is designed as an incentive for key network participants that integrate its features into their applications and as a reward for contributing to network consensus, staking, and governance.
FIO Protocol Fees
Each transaction within the FIO ecosystem has an associated fee in FIO tokens. To make for a smooth user experience, the majority of transaction types are covered upfront upon registering a FIO Crypto Handle. In return, users receive a set number of transactions per year that they can freely use without spending additional tokens. Additionally, the integrator (wallet or exchange) may select to cover the cost of registering Handles and their included bundled transactions on behalf of users. FIO has 21 active and 21 standby block producers (BPs). The 42 BPs set protocol fees and vote on protocol changes.
Governance
Anyone may become a BP, but in order to produce blocks (as one of the 21 active validators) or set fees and earn rewards (as a standby validator), BPs must earn a top spot by voting power. Blocks are produced in rounds of 126. At the beginning of each round, 21 BPs are eligible to enter the active validator set, providing ample opportunity for BPs to become active should a new BP with significant ties to major stakeholders decide to contribute to network consensus. Ultimately, BPs are responsible for modifying system contracts and enacting protocol changes. A minimum of 15 BPs (i.e., greater than two thirds of the active validator set) must approve a proposal in order for it to pass.
The Foundation for Interwallet Operability (FIO) is allocated 5% of the protocol fees for running a DAO to coordinate protocol development activities with independent developers and contributors. The majority of entities participating in the DAO are wallets and exchanges that have joined the FIO consortium on a voluntary basis. In doing so, these entities participate in the governance process by signaling their support for the development of new protocol features, before being brought to a block producer vote.
Voting Mechanism
To participate in FIO governance is to vote for network BPs. A FIO Crypto Handle is required, and tokenholders may either vote for block producers directly or delegate their voting power (number of tokens held in wallet) to active vote proxies. If a wallet or exchange wishes to participate as a network proxy, they act as the default governance proxy for the FIO tokens held in their users’ wallets. Prominent FIO stakeholders can use this mechanism to contribute to network decision-making.
FIO Improvement Proposals (FIPs) are publicly available for review on GitHub prior to BP vote. Feature proposals funded by the foundation require both review and consent to be prioritized on the roadmap. Considering that the protocol is open-source, self-funded FIPs may also be brought forth to BP vote at community member discretion.
FIO Staking and Rewards
FIO token staking went live in January 2022 and is available in partner wallets for users that have voted (or proxied) towards at least one BP. If a user stakes from a registered integrated wallet, the organization receives 11% of stakers’ rewards. Staking rewards may be redeemed upon request while the original staked amount has a 7-day cool-down period.
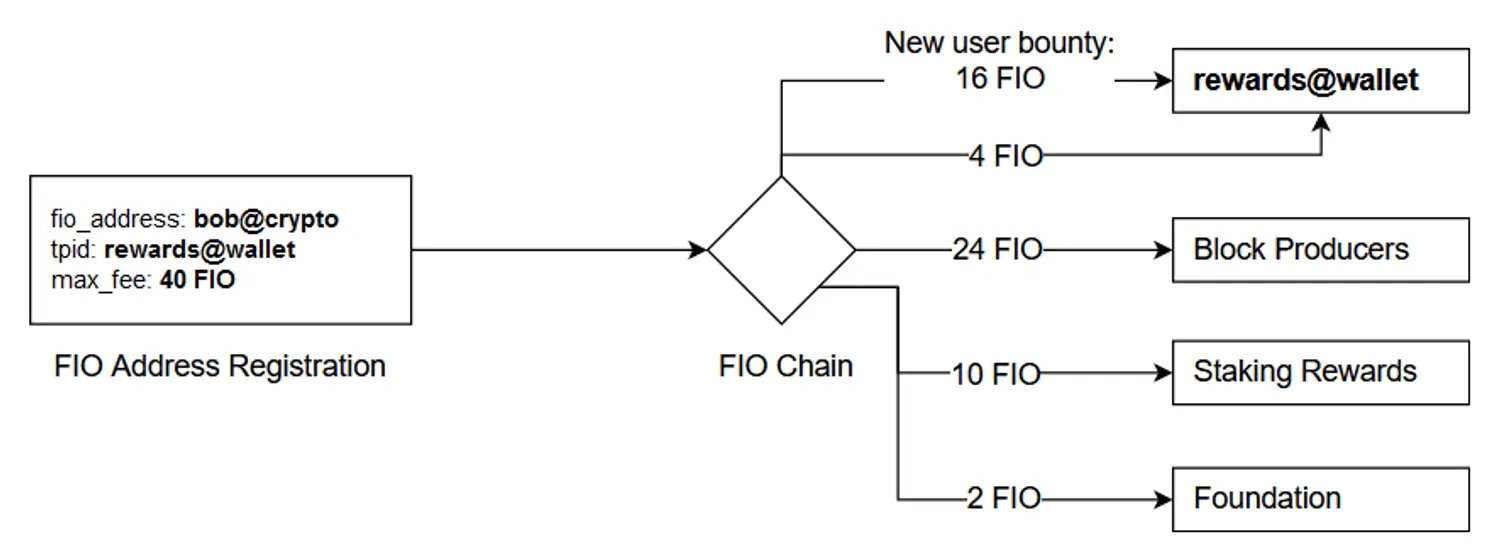
FIO’s fee mechanism rewards stakers with 25% of the protocol fees, while BPs earn 60%. Aside from BPs and stakers, 5% is reserved for the foundation, and 10% is distributed to integration partners. If there aren’t enough protocol fees to reward participants, FIO is drawn from reserves to subsidize BPs and stakers. A total of 20 million FIO (2% of the total token supply) is set aside in the BP reserve. If less than 50,000 FIO is collected in fees for BPs in a 24-hour period, tokens from the reserve will be supplemented to hit this cap until the reserve has been diminished. Similarly, 2.5% of the total token supply (25 million FIO) is set aside in the Staking Reward Reserve to ensure that staking rewards amount to 25,000 FIO per day amongst stakers, until this reserve is exhausted. Thanks to FIO’s incentive mechanism and decentralized business model, the benefits are spread to all ecosystem participants.
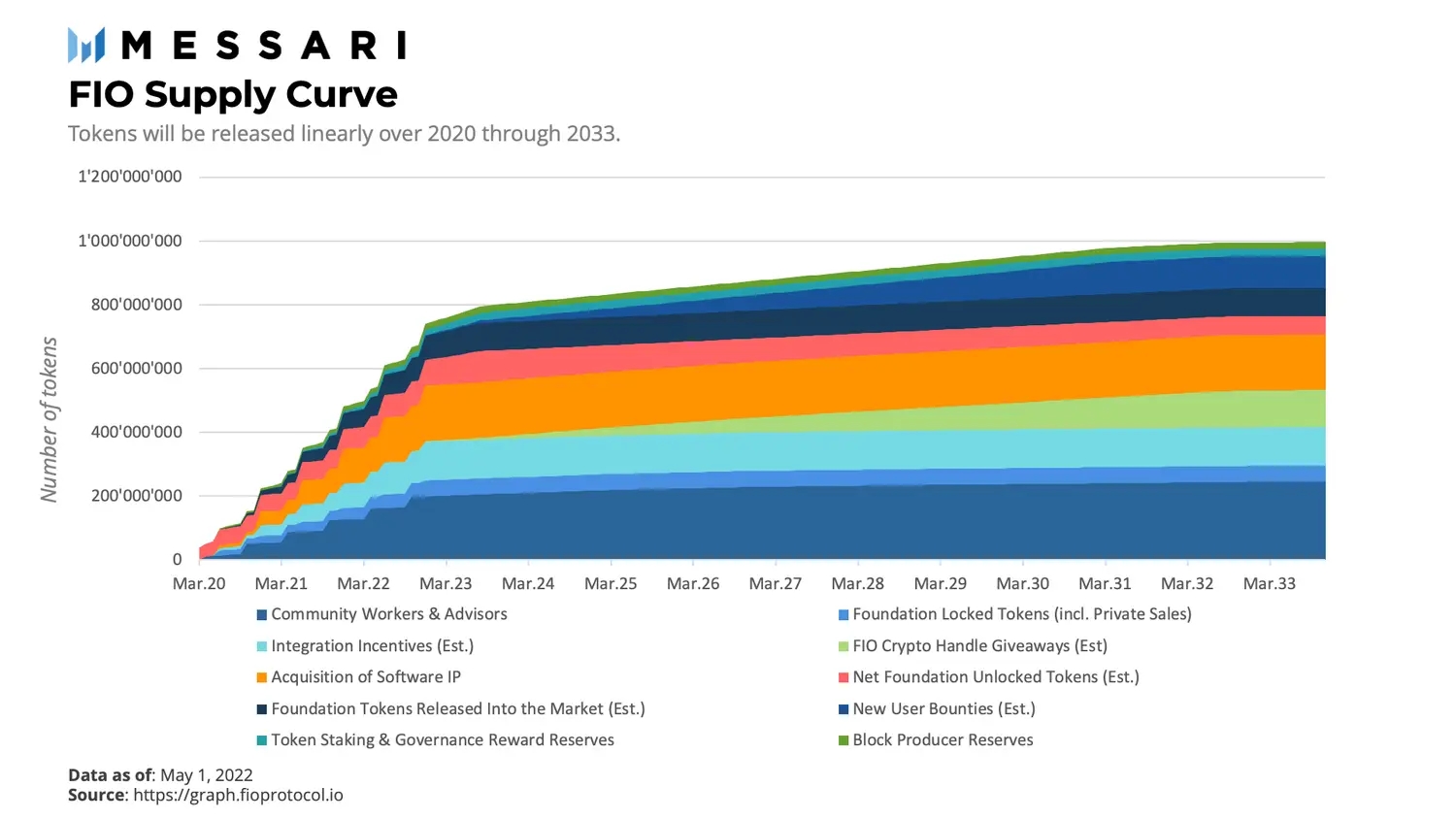
Supply Curve
The FIO token was launched independently of funding. A total of 50,000,000 FIO tokens were initially set aside and were subsequently allocated to the foundation. The token supply has a maximum of 1,000,000,000 FIO: 648,746,346 (65%) tokens were minted at Mainnet launch and 341,253,654 (34%) tokens are being minted over time. The foundation’s allocation (9% of the total token supply) will be fully unlocked by December 2022. Although locked foundation tokens were not programmatically restricted from voting for BPs, the foundation has abstained from voting at the time of writing. The remaining tokens are set to be released linearly through 2033 as depicted below.
FIO Ecosystem
Integration and Listing Agreements
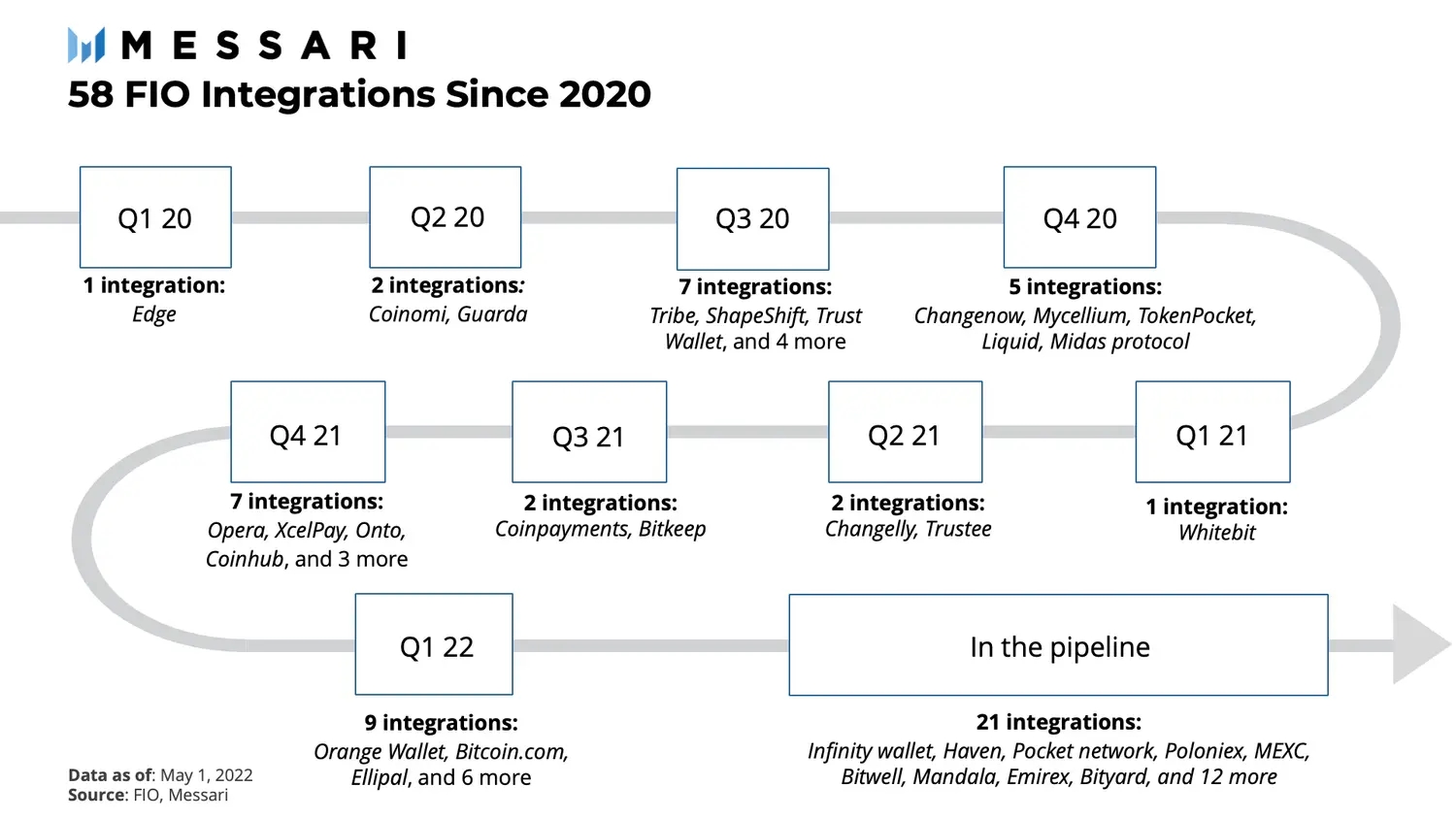
Since Q1 2020, 64 projects have joined or are in the process of joining the FIO ecosystem. Notably, 58 of these are FIO integrations into crypto products, while the remaining 13 are FIO listings for trading. The FIO rewards and incentive scheme is designed to encourage more projects to integrate FIO into their product offerings. The goal is for FIO-integrated products to have a substantial voice in governance, considering FIO is a usability protocol built for cryptoapplication providers.
Crypto applications such as wallets, exchanges, staking platforms, and crypto payment processors that integrate with the FIO Protocol are entitled to a number of rewards over and above fee distributions and staking rewards. A pool of 125 million FIO (12.5% of the total token supply) is allocated for rewarding integrators. Integrators receive an additional 40% on top of fees for facilitating the registration of new Crypto Handles and Domains. These rewards will be distributed until this reserve is exhausted.
The foundation also subsidizes fees for registering Crypto Handles and Domains on behalf of an integrated product’s users. Based on the number of users, the foundation awards wallets and exchanges with grants from $10,000–500,000. FIO occasionally airdrops tokens for wallets with a large number of users. As a result, the number of integrations has grown steadily over the past 2 years, and 21 integrations are in the pipeline.
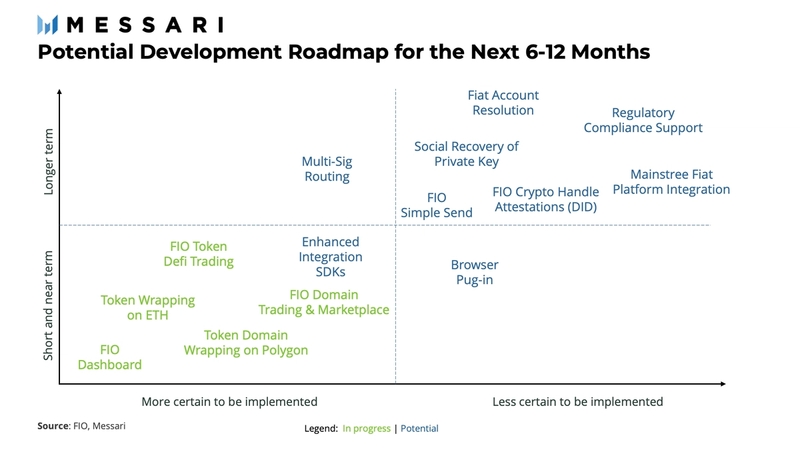
Potential Development Roadmap
Code development proposals are discussed, voted upon, and executed by the FIO community of developers. A summary of current and potential developments is graphically depicted below.
The current focus is on initiatives that simplify integration and help increase FIO adoption. On the wallet and exchange integration side, the top priority is the enhancements to the integration of software development kits. In terms of user experience and increased user adoption, a further simplification of the send feature is top of the list. In the long run, fiat account resolution and integrations appear to be important milestones toward large-scale adoption.
FIO Competition and Main Challenges
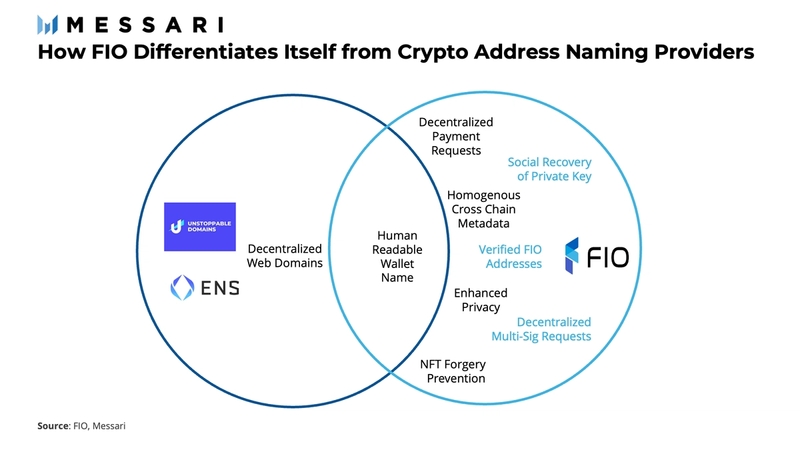
While the wallet naming space is relatively crowded, FIO’s main value proposition stems from improved user experience and its ease of integration with other crypto products. When compared to established players such as Ethereum Name Service and Unstoppable Domains, FIO distinguishes itself by being more than just a wallet naming service. In addition to wallet naming, it offers payment request functionality, encrypted payment data, and NFT signatures. That being said, emerging players such as Request Network are starting to offer payment request functionalities. While Request Network is currently limited to Ethereum, Polygon, Celo, Fantom, and NEAR, it is expected to expand its list of supported blockchains. However, FIO clearly differentiates itself through its modular design: FIO was built to be interoperable with any blockchain.
Moving forward, FIO needs to overcome several key challenges.
First, FIO must offer a smoother integration experience to increase the number of integrations with existing wallets and exchanges. Currently, partner developers need ~240 hours to integrate FIO’s full suite of functionalities. Recent efforts on developing a FIO Dashboard and a FIO Send API are set to significantly reduce partner integration work time to less than 20 hours. As more wallets and exchanges join the FIO ecosystem and best practices are established, the integration process will become more streamlined.
Second, FIO adoption is dependent on increasing usage frequency. FIO adoption could be jump started by creating behavioral hooks driven by habit-forming features, coupled with the continued adoption of DeFi.
Third, as the space inevitably becomes more crowded, it will be important for FIO to cement its core value proposition to differentiate itself from other providers. That being said, the foundation has expressed a willingness to work collaboratively with a leading domain space competitor should one emerge. Its goal in this cooperation is to promote the seamless operation of FIO Crypto Handles in a decentralized domain namespace system, subject to block producer approval. If accomplished, FIO would position itself as the standard usability layer for transacting digital assets in the long term.
Conclusion
In a multichain world, users need an easy way to send and receive assets across blockchains. FIO aims to enable a homogeneous user experience that rivals Web2 usage without compromising on decentralization. It simplifies the sending, receiving, and requesting of digital assets. As of May 1, 2022, there were over 704,000 FIO Crypto Handles registered from over 58 partner integrations. The real test for FIO is to grow enough to achieve wide-scale community adoption as crypto becomes mainstream.
This report was commissioned by FIO, a member of Protocol Services. All content was produced independently by the author(s) and does not necessarily reflect the opinions of Messari, Inc. or the organization that requested the report. Paid membership in Protocol Services does not influence editorial decisions or content. Author(s) may hold cryptocurrencies named in this report.
Crypto projects can commission independent research through Protocol Services. For more details or to join the program, contact ps@messari.io.
This report is meant for informational purposes only. It is not meant to serve as investment advice. You should conduct your own research, and consult an independent financial, tax, or legal advisor before making any investment decisions. The past performance of any asset is not indicative of future results. Please see our terms of use for more information.
Last updated